Neurofilament light IMR Reagent
“MagQu” Neurofilament light IMR Reagent is designed for quantitative measurement of Tau protein concentration in human plasma by immunomagnetic reduction (IMR) assay. The reagent can be used with MagQu’s Magnetic Immunoassay Analyzer XacPro-S system.
This assay enables early-stage neurological disease research with ultra-high sensitivity and low interference.
Features
Quantify NfL in the sample easily, rapidly, and accurately
Magnetic Nanoparticle
Dextran layer
For Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Parkinson’s disease (PD), Huntington disease (HD) research and for in-vitro diagnosis use
Specifications
Sample type: Human Plasma
Sample volume: 60 μl
Assay time: 5 hours (36 channels in XacPro-S)
Use application: In vitro diagnostic
Detection methods: ImmunoMagnetic Reduction (by analyzer XacPro-S with magnetic reagents)
Sensitivity
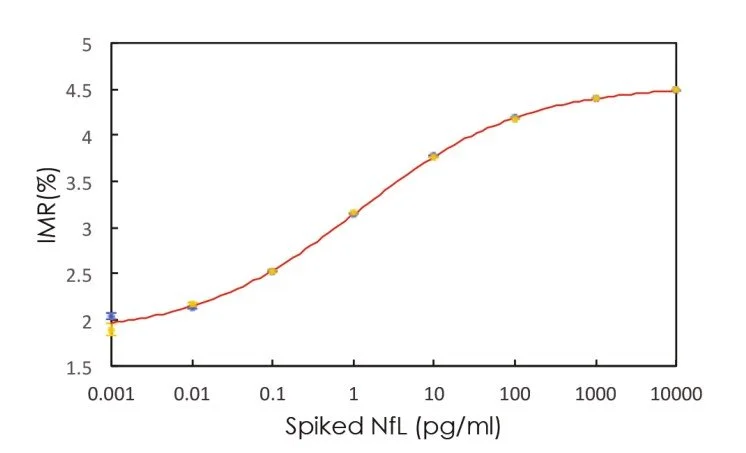
Detection Range: 0.01 - 100 pg/ml
Low detection limit: 0.18 fg/ml
IMR standard curve of NfL
Description
Intended Use
“MagQu” Neurofilament light IMR Reagent is used to quantitatively measure neurofilament light(NfL) in human fluid specimen, such as plasma, serum or CSF.
Use “MagQu” Neurofilament light IMR Reagent only with the XacPro-S System (MagQu Co., Ltd.).
Introduction
Neurofilament light(NfL) is a specific cytoskeletal protein highly expressed in largely myelinated axons. Increased levels of NfL in CSF and blood are clinically useful biomarkers in many neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Parkinson’s disease (PD), Huntington disease (HD). 1,2
Principles of Test
“MagQu” Neurofilament light IMR Reagent is designed for rapid quantifying NfL by ImmunoMagnetic Reduction (IMR). We conjugate antibody on the surface of around 50 nm-in-diameter Fe3O4 magnetic particles. When the antibodies on the surface bind with NfL, the magnetic particles form clusters. Therefore, the ac susceptibility (Xac) of magnetic particles would be reduced in the adding ac magnetic field. By measuring the reduction of Xac, NfL can be easily, rapidly and accurately quantified.3
Reagent Properties
Precision
The NfL samples were measured in duplicate,
twice per day over 20 days. Two different NfL
concentrations were used for the tests. The
standard deviations of repeatability and within-lab
for various NfL concentrations ware obtained:
Interference (Specificity)
Plasma can contain interfering substances such as
hemoglobin, bilirubin, or intra lipid because of
common diseases, such as hemolysis, jaundice or
hypertriglyceridemia. Other bio-substances that
exist naturally in plasma, such as uric acid, rheuma-
toid factor, or albumin, are also interfering
substances. Other interfering substances include
drugs or chemicals in medicine that is used to treat
inflammatory diseases, viral and bacterial infec-
tions, cancers and cardiovascular disease. The level
of NfL in each of these pools was then determined
and normalized to the level without the respective
substances.
Expected Value
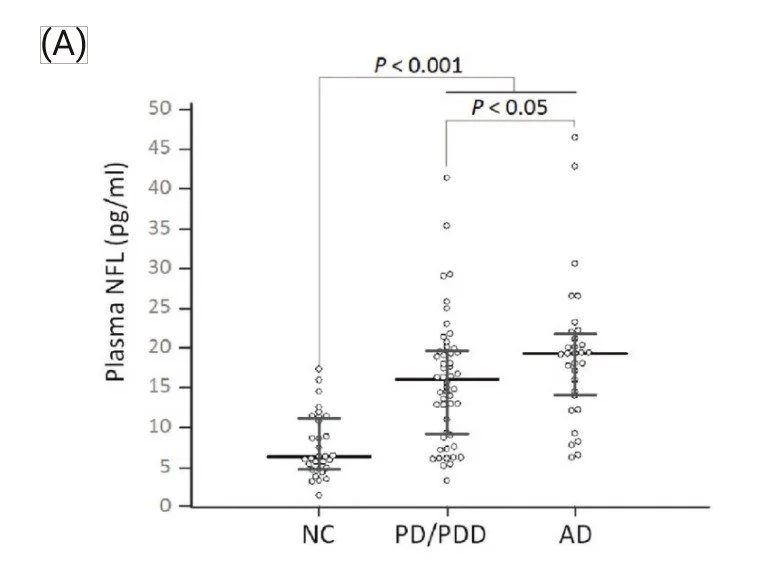
In this work, thirty-one normal controls (NC), fifty-two patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD) or PD dementia (PDD), and thirty-one patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) were enrolled at National Taiwan University Hospital and Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital.
(A) Measured NfL concentrations in human plasma using IMR and (B) ROC curves used for differentiating various diagnostic groups (NC: normal control, PD: Parkinson’s disease, PDD: Parkinson’s disease dementia, AD: Alzheimer’s disease, dementia: PD/PDD+AD).
Application References:
Liu HC, Lin WC, Chiu MJ, Lu CH, Lin CY, Yang SY. Development of an assay of plasma neurofilament light chain utilizing immunomag-netic reduction technology. PLoS One. 2020 Jun 12;15(6):e0234519.