GFAP IMR Reagent
“MagQu” GFAP IMR Reagent is designed for quantitative measurement of Tau protein concentration in human plasma by immunomagnetic reduction (IMR) assay. The reagent can be used with MagQu’s Magnetic Immunoassay Analyzer XacPro-S system.
This assay enables early-stage neurological disease research with ultra-high sensitivity and low interference.
Features
Quantifying GFAP in the sample easily, rapidly, and accurately
Magnetic Nanoparticle
Dextran layer
For traumatic brain injury and Alzheimer’s disease research and for in-vitro diagnosis use
Specifications
Sample type: Human Plasma
Sample volume: 60 μl
Assay time: 5 hours (36 channels in XacPro-S)
Use application: In vitro diagnostic
Detection methods: ImmunoMagnetic Reduction (by analyzer XacPro-S with magnetic reagents)
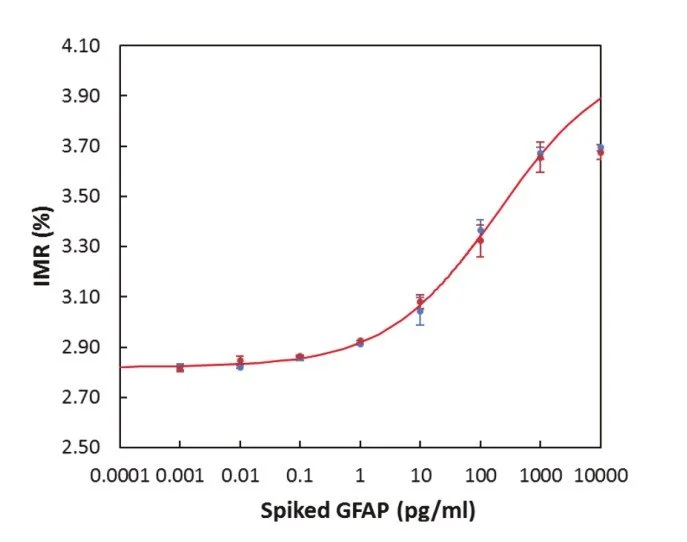
Sensitivity
Detection Range: 1 - 100 pg/ml
Low detection limit: 31.4 fg/ml
IMR standard curve of GFAP
Description
Intended Use
“MagQu” GFAP IMR Reagent is used to quantitatively measure glial fibrillary acidic protein(GFAP) in human fluid specimen, such as plasma, serum or CSF.
Use “MagQu” GFAP IMR Reagent only with the XacPro-S System (MagQu Co., Ltd.).
Introduction
Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) is the main constituent of the astrocytic cytoskeleton, which plays an important role in the structure and mobility of astrocytes and can affect astrocyte function. The amount of GFAP in the blood begins to rise in the early stages of Alzheimer's disease. Symptoms of astroglial cell deposition can be a sign of the onset of early events in AD. Therefore, GFAP can be used to predict the future onset of Alzheimer's disease, mild cognitive impairment, and changes in the structural features of brain MRI in the elderly. 1,2
Principles of Test
“MagQu” GFAP IMR Reagent is designed for rapid quantifying GFAP by ImmunoMagnetic Reduction (IMR). We conjugate antibody on the surface of around 50 nm-in-diameter Fe3O4 magnetic particles. When the antibodies on the surface bind with GFAP, the magnetic particles form clusters. Therefore, the ac susceptibility (Xac) of magnetic particles would be reduced in the adding ac magnetic field. By measuring the reduction of Xac, GFAP can be easily, rapidly and accurately quantified.3
Reagent Properties
Precision
The GFAP samples were measured in duplicate,
twice per day over 20 days. Two different GFAP
concentrations were used for the tests. The
standard deviations of repeatability and within-lab
for various GFAP concentrations ware obtained.
Interference (Specificity)
Plasma can contain interfering substances such as
hemoglobin, bilirubin, or intra lipid because of common
diseases, such as hemolysis, jaundice or hypertriglyceri-
demia. Other bio-substances that exist naturally in
plasma, such as uric acid, rheumatoid factor, or
albumin, are also interfering substances.
Other interfering substances include drugs or chemicals
in medicine that is used to treat inflammatory diseases,
viral and bacterial infections, cancers and cardiovascu-
lar disease. The level of GFAP in each of these pools
was then determined and normalized to the level
without the respective substances.
Expected Value
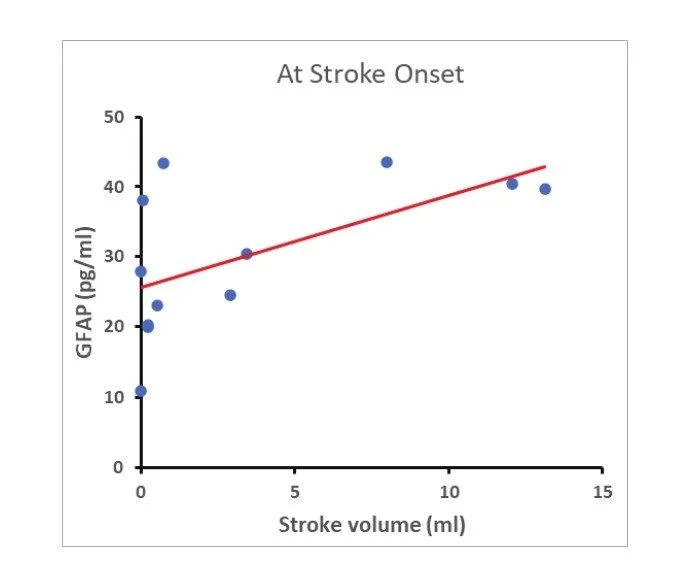
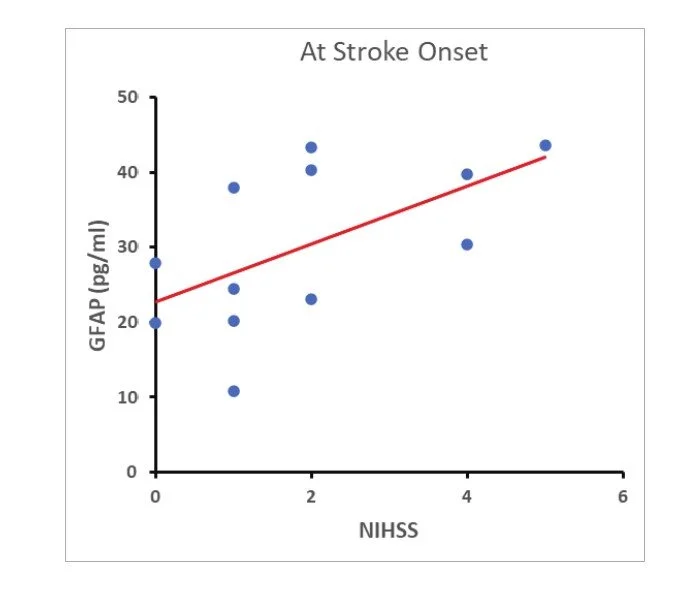
Plasma samples from patients with ischemic stroke (n = 12) were collected for GFAP assays using the IMR GFAP reagent. Plasma samples were collected from stroke patients on the 3rd-5th day after the onset of stroke.
Fig. 1 Significant correlations of Stroke volume and plasma GFAP levels
Fig. 2 Significant correlations of NIHSS Score and plasma GFAP levels