UCH-L1 IMR Reagent
“MagQu” UCH-L1 IMR Reagent is designed for quantitative measurement of Tau protein concentration in human plasma by immunomagnetic reduction (IMR) assay. The reagent can be used with MagQu’s Magnetic Immunoassay Analyzer XacPro-S system.
This assay enables early-stage neurological disease research with ultra-high sensitivity and low interference.
Features
Quantifying UCH-L1 in the sample easily, rapidly, and accurately
Magnetic Nanoparticle
Dextran layer
For traumatic brain injury and Alzheimer’s disease research and for in-vitro diagnosis use
Specifications
Sample type: Human Plasma
Sample volume: 60 μl
Assay time: 5 hours (36 channels in XacPro-S)
Use application: In vitro diagnostic
Detection methods: ImmunoMagnetic Reduction (by analyzer XacPro-S with magnetic reagents)
Sensitivity
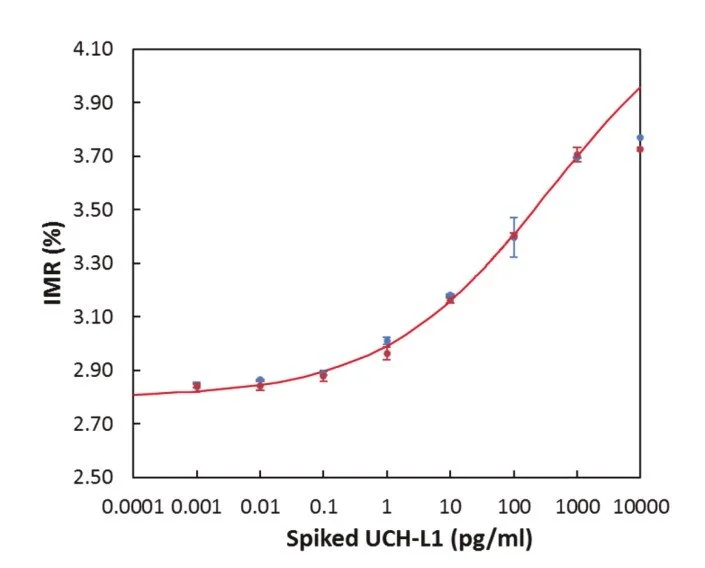
Detection Range: 1 - 100 pg/ml
Low detection limit: 3.3 fg/ml
IMR standard curve of UCH-L1
Description
Intended Use
“MagQu” UCH-L1 IMR Reagent is used to quantitatively measure ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L1(UCH-L1) in human fluid specimen, such as plasma, serum or CSF.
Use “MagQu” UCH-L1 IMR Reagent only with the XacPro-S System (MagQu Co., Ltd.).
Introduction
Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCH-L1) is an extremely abundant deubiquitinating enzyme in brain, which involved in the elimination of misfolded proteins. UCH-L1 is not essential for neuronal development, but is necessary for maintenance of integrity. Recent studies have found an association between UCH-L1 dysfunction and neurodegenerative diseases. In previous studies, UCH-L1 expression was found to be decreased in patients with ischemic injury and Alzheimer's disease. It is possible that UCH-L1 increases free ubiquitin expression by promoting ubiquitination and accelerates lysosomal degradation of amyloid β-synuclein or α-synuclein, which tend to accumulate when they are reduced. Over-expression of UCH-L1 has also been shown in mouse models to effectively delay the progression of Alzheimer's disease. Thus, UCH-L1 may be a pre-dementia process with the potential to predict the onset of dementia. 1,2,3
Principles of Test
“MagQu” UCH-L1 IMR Reagent is designed for rapid quantifying UCH-L1 by ImmunoMagnetic Reduction (IMR). We conjugate antibody on the surface of around 50 nm-in-diameter Fe3O4 magnetic particles. When the antibodies on the surface bind with UCH-L1, the magnetic particles form clusters. Therefore, the ac susceptibility (Xac) of magnetic particles would be reduced in the adding ac magnetic field. By measuring the reduction of Xac, UCH-L1 can be easily, rapidly and accurately quantified.4
Reagent Properties
Precision
PRECISION
The UCH-L1 samples were measured in duplicate,
twice per day over 20 days. Two different UCH-L1
concentrations were used for the tests. The
standard deviations of repeatability and within-lab
for various UCH-L1 concentrations ware obtained.
Interference (Specificity)
Plasma can contain interfering substances such
as hemoglobin, bilirubin, or intra lipid because of
common diseases, such as hemolysis, jaundice
or hypertriglyceridemia. Other bio-substances
that exist naturally in plasma, such as uric acid,
rheumatoid factor, or albumin, are also interfer-
ing substances.
Other interfering substances include drugs or
chemicals in medicine that is used to treat
inflammatory diseases, viral and bacterial infec-
tions, cancers and cardiovascular disease. The
level of UCH-L1 in each of these pools was then
determined and normalized to the level without
the respective substances.
Expected Value
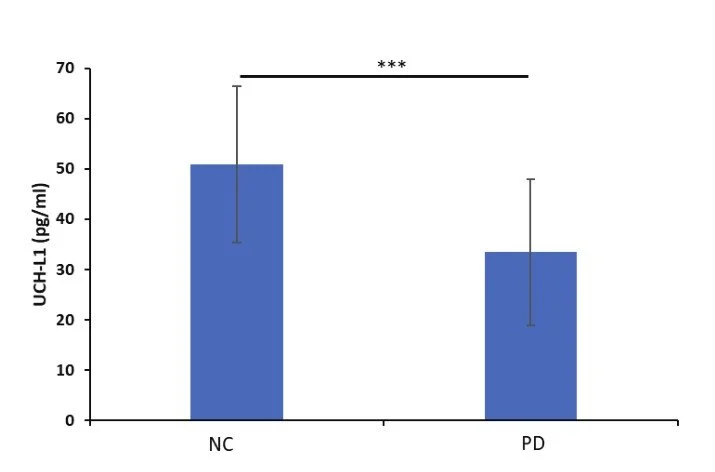
Plasma samples from normal controls (NC, n = 50) and from patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD, n = 63) were collected for UCH-L1 assays using the IMR UCH-L1 reagent.